Your organization has either; BEEN attacked, is currently BEING attacked or WILL BE attacked by cyber criminals. Our mission is to provide you the knowledge, the vision, and the solutions to secure your assets. With cyber-attacks becoming more and more prevelent in recent months (Petya, WannaCry, Google Phish), businesses, schools, and organizations alike are scrambling to find the right way to secure their assets. Not all cyber attacks are created equal and in this post we hope to shed some light on the "Big 3" types of cyber attacks, malware, ransomware, and phishing attacks. We will show you examples of each attack and share with you a few tips from on how you can prepare yourself for the next major cyber attack.
Major Types of Cyber Attacks
Malware
What is it: Malware is a general term for malicious software. Malware includes viruses, worms, Trojans and spyware. Many people use the terms malware and virus interchangeably. Malware is more of an umbrella term used to describe a lot of different cyber attacks.
How does it work: One example of malware is a trojan horse. A trojan horse is a virus that poses as legitimate software. As you launch the program it may appear to be working in the way you hoped, but what you don't realize is that it is slowly infecting your computer until it loses functionality.
Prevention: Due to the expansiveness and diversity of malware attacks it's hard to pinpoint one specific way to protect against all malware attacks. Often companies find themselves having to go to multiple security providers to protect from all of the different malware attacks. It is rare to find all of the protection in one place, but with Sophos' Synchronized Security you can be protected from it all. Synchronized Security protects you from your firewall to your endpoint and everything in between. For more information see: Sophos Intercept X Protects against Malware.
Example: Let's say one of your employees or co-workers reads this article and thinks "wow, I better install an anti-virus program!" They go online and find one that looks legitimate only to find out it is infected with a trojan horse virus. You may not realize this at first but you will as the virus slowly duplicates itself until your computer is so slow and infected there is essentially nothing left you can do except hope to copy your data in time before you computer loses functionality.
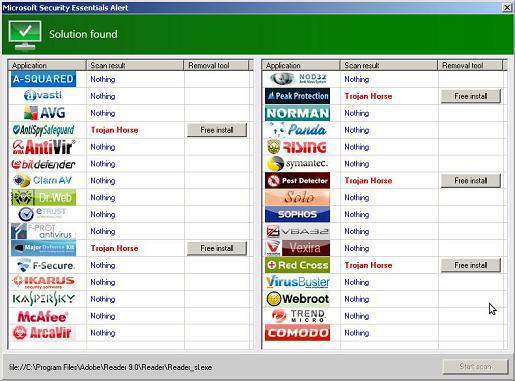
Ransomware

What is it: Ransomware is software that denies you access to your files or computer until you pay a ransom.
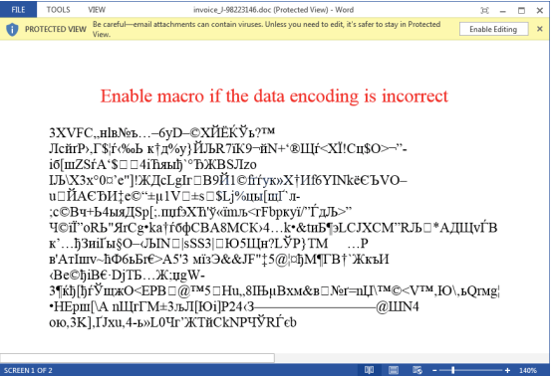
How does it work: Ransomware always requires that the user complete a call to action. A call to action is when someone clicks on an infected link online, or would enable editing on a infected document such as the one shown below.
Prevention: Keep your system updated. That little notification in the bottom right corner of your screen can be important to protecting yourself from ransomware attacks. Cyber criminals often target users who haven't updated their computers. Another important means of protection is backing up your documents. Make sure you have copies of all your important documents in case you ever get infected and can't retrieve them. Employees will never fail at downloading/opening suspicious content so you should look into a more robust system of protection as well. In the article, Sophos Intercept X Stops Ransomware, we show you Sophos' solution to ransomware protection.
Example: An employee or co-worker downloads the document below off of a website. If the user were to enable editing on this document, the action would trigger a code which would encrypt valuable documents on your computer and would only give you access to these documents again upon paying a ransom, usually through anyonomis crpytocurrency such as bitcoin. The user is then faced with the decision of losing valuable documents, or essentially writing the cyber criminal their paycheck for an average of a few hundred dollars.
Phishing

What is it: Phishing refers to the process of deceiving recipients into sharing sensitive information with an unknown third party (cyber criminal).
How does it work: A cyber criminal will strategically pick companies susceptible to cyber attacks. It doesn't matter if you are a large corportation, small business, school, or non-profit, they will target you. After picking an organization, the hacker will do some research about the company so they can create a convincing email to send to employees. Once they are ready to send the email, they will make the final touches by either asking for sensitive information or embeding a dangerous link in the email, allowing them to encrypt your documents. After the cyber criminal sends the email, the criminal waits and watches as employees of the targeted organization respond to their email with the sensitive information the criminal is looking for.
Prevention: Prevention first starts with educating the members of your organization on how phishing works. Encourage employees and co-workers to be suspicious of emails from unfamiliar recipients or emails asking for sensitive information. However, education is not enough. There will always be that one employee who can't help but click on the bait in the email to see what is going on. According to Brandon Vancleeve, Vice President at Pine Cove Consulting, "30% of recipients open phishing email links." What you really need is a comphrensive cyber-security solution. To learn more about our cyber-security solution, contact us.
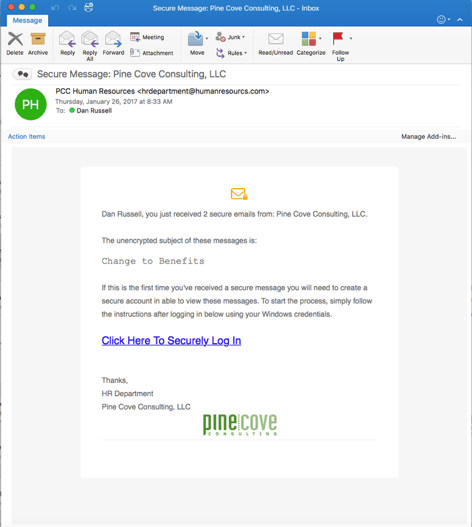
Example: Below is a common example of what a phishing email looks like. It usually looks like it is coming from someone you know, however, upon examination of the email address, you may find that it is unfamiliar. The email will direct you to click on a link which will then ask for sensitive information. If an employee continues, the hacker will have access to that information and will then use it to steal your assets. Common phishing attacks lead to loss of extremely personal information such as social security numbers and credit card information.
Conclusion
These are the major types of cyber attacks you need to know about. Cyber criminals are smart though and are continually coming up with new ways to get their work done. No longer can organizations turn a blind eye to the threat of cyber security. It is time to for organizations to protect themselves and fight back against cyber crime.
Want more information? View our webinar on Sophos' Synchronized Security solution. Also be sure to view our other blog posts on cyber-security.












